Ali Akbar Mottahedi
Industrial Metallurgy and New Processing group, Department of Advanced Materials and Renewal Energies Iranian Research Organization for Science and Technology (IROST) Forsat St. 71, Ferdoosi Sq., P. O. Box: 15815-3538 (Iran)
Article Publishing History
Article Received on :
Article Accepted on :
Article Published :
Article Metrics
ABSTRACT:
Rolling is an important process in metal forming because of high productivity and production tonnage of wrought metals. Hence, any interruption in rolling line or wastage has large costs. So, technological research or any change in rolling process is difficult along with a high risk of cost in industrial scale. Thus, rolling simulation by computer and using of software could make rolling research easy. Analysis of pressure profile on rolls and maximum rolling pressure in flat rolling process is very important in metal forming investigations. It is also significant in controlling of force, power, rolls, rolling process and so on. The author of this paper had a project in the field of computer simulation of flat rolling by making software. This paper is about to show the simulation of flat rolling process by using of that software and experimental industrial experience. Analysis of the rolling pressure profile and maximum rolling pressure is also shown for an Aluminum alloy in this software.
KEYWORDS:
Rolling computer simulation; rolling pressure profile; Rolling pressure; rolling process; flat rolling
Copy the following to cite this article:
Mottahedi A. A. Simulation of Flat Rolling and Analyzing of Rolling Pressure Profile. Orient. J. Comp. Sci. and Technol;1(1)
|
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Mottahedi A. A. Simulation of Flat Rolling and Analyzing of Rolling Pressure Profile. Orient. J. Comp. Sci. and Technol;1(1). Available from: http://www.computerscijournal.org/?p=2019
|
Introduction
One of the most important methods of metals forming process is rolling, with high production tonnage and high velocity. The production capacity of rolling process is more than all other processes in industry¹. Rolling is a continuous process and has been divided to two types. The first process is called caliber rolling, which is used for rolling of square ingot to I beams, rods, angles and so on. The second process is called flat rolling which is used to produces foil, sheet and plate of slab. Flat rolling process is used in bulk metal forming of steel, Aluminum, copper and other metals. Recently, rolling is used also to produce other materials such as composites, plastics and so on. The capacity of steel rolling industrials is about millions tons per years. This capacity is about 100,000 tons for non ferrous rolling industry.
Because of high capacity of flat rolling, the most cost in rolling industry, is the stopping cost of production line. Sometimes its cost is about one
million dollars per day. Wastages are the other important cost of rolling industries. Because of continuity of production line and coiling form of sheet
products any quality or technological problems can makes, wastages all of the coil, which is weighted about more than 20 tons sometimes. Any technological problem that leads to wastages of products, or worse than it, stopping production line could make damage in industry. Hence, practical
research or technological change in rolling industry is complicated and has high risk of cost. Therefore computer simulation of flat rolling is important.
The researchers or engineers can modify their rolling process by computer at first, then they can use the results in the rolling process practically. This simulation reduces the cost of rolling examine as well as the time of technological research.
The author of this paper had a project for computer simulation of flat rolling and he makes software by using theoretical aspect of metal forming, experimental data and experience in industrial rolling technology. Analysis of pressure profile on rolls and other useful information and computation of flat rolling process which are significant in controlling of force, power, torque, rolls, crown, and so on, are analyzed by this computer program. This paper is written to exhibit the computer program and its using in R&D, quality control, planning and technology of flat rolling process industry.
Procedure
By using theoretical and experience rolling relations were gathered and getting together. to make relations of initial, data of rolling. It was some up more than 200 formulas in this stage by using of geometrical, mathematical and experimental formulas¹
- Effective factors of the flat rolling process were recognized and categorized, according to practical engineering and research experiences.
- The effect of data or effective factors in the rolling process from the view point of mathematics and the principles of metal forming has been examined and are presented by mathematical equations.
- The engineering software has been made for all mentioned calculations by fundamental studying of flat rolling.
- Logical and mathematical controllers were added to the software to operate in a precise and logical way.
- Experimental and engineering controllers were added to the software to inspect the input dada in an extensive area.
- By using practical experiments, theories and rolling calculations, some recommendations and forecasts were added to the software in order to exhibit some messages in relation with forecast of errors and technological problems to user according to input assumptions.
- The software has attained experimental level by gathering real data from an Aluminum flat rolling factory and using the results of Aluminum alloy rolling. Results of real rolling show the same consequences in comparison with software’s predictions.
- Sub program have been used in the software. Hence, it has been tried to divide the program to different collections and then to joint them together. This method of program writing has many advantages, and software experts use it for long programs.
- In the prepared simulation, the speed and exactness of analysis and calculations are chosen by using a coefficient at first.
- Von Misses theory is used as effective stress analyzing for metal forming in the software.
Argument and conclusion
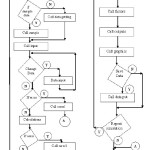
The computer program flowchart has been shown in figure 6, and a sample of software performance and analysis have been presented in
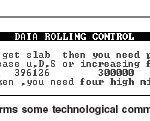
figures 1 to 5. Figure 1 shows the first page and figure 2 shows data login page. In page 3 you will find some technological comments after data login
by software to inform analyzing. Analyses of maximum rolling pressure, rolling pressure profile and instantaneous plate thickness versus bite angle
are shone in figure 4 which have very useful results for rolling specialists. As it could be seen, the pressure profile of flat rolling has a pick which in
this type of process is more near to exit. This computer program was confirmed by real practical data and has been examined in industrial scale. The
simulated software can be used in production line and flat rolling industries in order to perform in research, quality control and production sections
of rolling industries. It could be also used by universities for teaching rolling course, or metal forming.
Acknowledgement
Helpful discussion with the engineers of Honsel Company in Germany, especially Mr. Lotz, Beretaue, Zeh, and providing beneficial data from
them is highly acknowledged. In addition, thank professor doctors Matin from Shiraz University, Salehi, Taghiee, Abrinia and Mirdamadi from
Elmosanat University, the colleagues in IROS- Arak, engineers and colleagues of Arak Aluminum rolling company.
References
- William F. Hosford, Robert M. Caddell, “Metal forming Mechanics and Metallurgy”, prentice- Hall (1993).
- Dieter G.E., “Mechanical Metallurgy”,MC Graw Hill (1988).
- Rowe G.W., “principals of industrial Metalworking processes”, McGraw-Hill Education (2006).
- Tselikov, Nikitin, Rokotyan, “The Theory of Lengthwise Rolling”, 1981, Mir Publishers
- Johnson & Mellor, “Engineering plasticity”, John Willey & Sons (1985).
- “Computer Simulation in Materials Science”, A.S.M (1988).
- “Advances in cold Rolling Technology”, London, The Institute of Metals (1985).
- “Aluminum Technology” London, the Institute of Metals (1986).
- Lark Eustace C., “The Rolling of strip, sheet and plate”, Champan and Hall LTD (1967).
- “Hand book of Metal Forming”, MC Graw Hill (1985).
- “Aluminum data handbook” 9.ED, Aluminum Association (1988).
- “Fundamental of the theory of rolling”, 1965, Mascow Metallurgiya
- Chen B.K., Thomson P. F. & Choi S. K., “Computer modeling of microstructure during

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.