Challenges of E-Library Services in Tertiary Institutions of Ebonyi State –Nigeria
Introduction
E-library is synonymous to both virtual library and digital library which is a library where services or collections of electronic resources are entirely virtual and access through internet service. An E-library does not have a physical space where interested persons can visit to access information or academic resources, instead distribution of resources are done electronically virtually. It is also called a paperless library. Digital libraries,E-libraries or virtual libraries are characterized by the following features as noted by (Costabile and Semeraro, (1998);
Access to information over a network
Facilitate immediate and simultaneous access to information
They are interactive, i.e. support 2 ways communication with the users,
They exist in multimedia format of text, video, graphics, sound and animation. Above all,
It increases speed and effectiveness in finding information
And also,decrease mental effort put into searching of information in the internet.
According to Irokwe (2001), a digital library
is a library that harnesses digital technologies as infrastructure to search,
collect, organize, store and distribute cultural, historical and scientific
information whether it is text, visual images or sound. This means that all the
operations/services of the traditional library are digitized or computerized. Such
operations include selection and acquisition, cataloguing and classification
etc. It comes into existence due to inconveniences of old system which is traditional
library system. The E-library contains resources that are either born digital
or digitized resources that pass through the process of transformation from
hard to soft copies.
Review of Related Literatures
There
is no single definition for E-libraries. Within the context of libraries,
digital libraries may be viewed as technical services performed electronically
with an entirely electronic application. The E-libraries are “a set of electronic
resources and associated technical capabilities” and that are designed to serve
specific users community, (Buckland’s electronic library, 2012). Trivedi (2010)
defined digital library as “a library in which collections resources are stored
in digital formats (as opposed to print, microform,or other media) and
accessible by computers.” Aman and Norliyanan (2002) stated that an electronic library
also refer to as digital library or digital repository focused on collection of
digital objects that can include text, visual material, audio material, video
material, stored as electronic media formats (as opposed to print, micro form,
or other media), along with means for organizing, storing, and retrieving the
files and media contained in the library collection,” They also viewed it as “a
potentially virtual organization, that comprehensively collects, manages and
preserves for the long dept of time rich digital content, and offers to its
targeted user communities specialized functionality on that comprehensive
codified policies.” Universally, Digital libraries are perceived as libraries
in which all information resources are available in computer process through
which acquisition, storage, preservation, retrieval and dissemination of
resources are carried out using digital technologies. Mutula and Ojedokun
(2008) noted that it is a library that contains no conventional print
information resources, but electronic books, journals and newspapers. They
further observed that the digital library may not occupy a physical space,
where as users need to go and gain access to its electronic resources.
In
another development, Li and Furht (2014) stated that digital libraries are
systems that combine the machinery of digital computing storage and
communication, in which the content, and software needed to reproduce, emulate
and extend that services of collecting, cataloguing, finding and disseminating
information offered by traditional libraries based on paper and other
materials.“They also viewed digital libraries as systems providing a community
of users with coherent access to a large, organized repository of information
and knowledge.” The ability of the user to access, reorganize, and utilize this
repository is enriched by the capability of digital technologies.
According
to Irokwe (2001), a digital library is a library that harnesses digital
technologies as infrastructure to search, collect, organize, store and
distribute cultural, historical and scientific information whether it is text,
visual images or sound. It also developed electronic catalogue of all library
materials, networking this catalogue, so that users not only in the library but
also from elsewhere can access it. Additionally, digital library includes the
digitalization of locally produced information and the establishment of
institutional repositories, to provide access to the scholarly material
produced by members of the university communities.
According
to Daniel (2002), Nancy Schiller was one of the first writers to use the
expression “virtual”. Schiller simply uses the term as “libraries in which
computer and telecommunication technologies make access to a wide range of
information resources possible.” All virtual libraries must, by virtue, be
electronic, but not all electronic libraries are necessarily virtual. It is
called ‘virtual’ because in a good electronic wide area networked library,Students
and lecturers from the tertary institution of Ebonyi state gets access to the
E-libraries services in distance areas without physical movement.
Fabunmi
(2009) added more light that the virtual library can consist of materials from
a variety of separate libraries that are organized in a virtual space using
computers and computer networks.
Powell (1994) defined VL as: “a library with
little or no physical presence of books, periodicals, reading space, or support
staff, that disseminates selective information directly to distributed library
customers, usually electronically.”
Omolaye
(2002) extended the definition to include access to electronic
resources in the university library not only through the Internet but also
other electronic/digital networks such as campus network or the intranet,
without the physical need of the concerned community i.e. staff, students etc
visiting the library. This is in line with the definition of Rosenberg (2005)
as “a library where information resources are made available and accessible
electronically, frequently over the internet.”
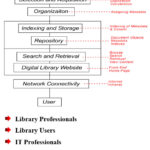
Components and community of Digital Library
Benefits of E-Libratires in Tetiary Institutions in Ebonyi State
The
following are the benefits of E-libraries to tertiary institution in Ebonyi
state;
Openness and Accessibility
College
and university librarians in tertiary institutions in Ebonyi state just as
their counterpart in other Tertiary institutions in Nigeria advocates for a new
system of scholarly publishing that broadens public access and encourages their
researchers to publish in open-access journals that can be produced at much
lower costs than commercial publications. Shifting from closed to public access
requires the cooperation of researchers and a rethinking of the tenure and
promotion system.Hence,E-library supports, encourages and promotes openness and
easy accessibility.
Support the Transformation to Online Learning:
As
a physical entity, the Ebonyi state tertiary institutions campus library is
typically perceived as the exclusive territory of the on-campus undergraduate
only. The virtual college library, which provides access to vast amounts of
digital content, is open to all campus constituents both full time
students,part time students,graduates,undergraduates,full time lectures ,part
time lecturers etc no matter where they may do their learning. Academic
libraries are well positioned to support online learners.There are other ways
in which we must support online learners, be it by providing online research
instruction or delivering hardcopy materials. As more students take online or
hybrid courses, the academic library infrastructure, honed for years to provide
remote access support, will be there to serve them, and to help the institution
make the transformation to digital education.
Support the Transformation to High Productivity
Students
don’t has as much time as they
likely to get to other very sensitive
and important works that needs attention.Keeping up with new technology alone
takes considerable time, and traditional higher education is in no position to
allow its community members to fall behind in putting technology to use for
learning and productivity. E-librarians are experts at transforming through
technology and also helping others learn to use technologies to save time on
tasks.Academic leaders should look to the campus library for support and guidance
in applying technology to improve productivity. Librarians are enthusiastic
partners in collaborating with others on campus to facilitate the
transformation to increased productivity.
Support the Transformation to Alt-Higher Ed
Higher education no longer needs to be delivered by one institution in a linear pattern to students. Instead, students will soon be able to earn credits across a spectrum of providers through the internate.Academic librarians are already contemplating how they can be “alt-librarians” for alt-higher ed. Providing research support, library instruction and other services in this setting brings new challenges, but academic librarians are accustomed to change and will evolve in this new alt-librarian role.
Promotion of Library use through Effective Services
The
main goal of digitization in academic library is to promote library use through
effective services. Local and international recognition and respect are partly
determined by quick accessibility to published works. Some highly productive
scholars globally have been found to be more information rich than their
counterparts. This implies that information adds significantly to the existing
knowledge of the users. The information resources and services available in
institutional information systems (library, archives, records offices, and
documentation centers) are digitized and create databases capable of supporting
research activities. The shift from print to electronic information means that
both academic staff and students in a University system must use these resources
for better quality, efficient, and effective research more than ever.
Digital
libraries are libraries that are extended and enhanced through digital
technology. Liand Furht (2014) noted that the important aspects of a digital
library that may be extended and enhanced include: The collection of the
library, The organization and management of the collections, Access to library
items and the processing of the information contained in the items, The communication
of information about the items.
They further stated that the objectives of digital libraries are: To speed up the systematic development of the means to collect, store, and organize information and knowledge in digital form, and of digital library collections.
To promote the economical and efficient delivery of information to all parts of society
To encourage co-operative efforts which leverage the considerable investment in research resources, computing and communication net-work.
To strengthen communications and collaboration between and among the research, business, government and educational communities.
To contribute to the lifelong learning opportunities of all people.
They
concluded that digital libraries distribute a rich coherent set of information
services (including selection, organization, access, distribution, and
persistence\) to users reliably and economically.
The
cardinal objectives of academic libraries are designed primarily to serve their
parent institutions most especially by meeting the teaching, research, and
learning needs through provision of the services (conventional and digital)
that can lead to an increase in the productivity of their students, teachers
and researchers. To buttress this, Trivedi (2010) stressed that digital
libraries posses unlimited storage space at a much lower cost, enhance
information users with coherent sources to a very large, organized repository
of information and knowledge.
Challenges of E-Library in Ebonyi State Tetiary Institutions
The preceding section has
glaringly exposed the digital library situation in Nigeria. However, the
development, and sustainability of digital libraries in Ebonyi state has the
following challanges:
Gross under Funding of E-Libraries
Gross under funding of E-libraries and education, as well as their near total neglect is one of such issues of serious concern. In addition, the resources and facilities of most libraries in the tertiary institutions of the state have deteriorated to a very low level, at times even non existence.This is due to under founding or neglect by the concerned bodies. Many libraries have no e-mail, fax, telephone and computer based services (Fabunmali, 2009).E-libraries in tertiary institutions of Ebonyi state are mere ghosts of their former self and in deplorable conditions this factor.
Power Supply
Another major constraint to digital libraries or E-libraries services in the tertiary institutions of the Ebonyi state is epileptic power supply.This is inherited from the nature of electric power supply in the entire country. Nigeria is a country characterized with constant power outage. This tends to have negative effects on all developmental projects, and clearly portrays a potential danger. Digital libraries cannot survive in this kind of unfortunate and ugly condition.
Information Communication Technology(Ict) Infrastructure
Developing and sustaining a viable digital library or E-library system is heavily reliant on the provision of proper ICT infrastructure and other infrastructures. Diso (2005) has noted that Nigeria is severely disadvantaged in the area of ICT components such as the hardware, software, international bandwidth services, e.t.c. all of which constitute a barrier to E-libraries. Although there is an impressive and steady progress in the telecommunications sector in Nigeria in recent years, a lot of efforts need to be made to ensure its sustainability even in all states of the federation.Also, The constant experience disruption in electricity power supply and also vandalization of telephone wires in these tertiary institution of the state affects digital libraries usage.
Unsteady Nature of the National Information Technology Policy
Another major hindrance to the success of digital libraries in Nigeria which Ebonyi state inherits in this era of global change is the unstable nature of the National Information Technology Policy that was approved in 2001. Diso (2008) observed that despite the national effort to promote ICTs that resulted in the setting up of the National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA), which was saddled with the responsibility of implementing the National Information Technology Policy, nothing much has been achieved regarding the IT policy. This has an adverse effect to all digital library or E-libraries initiatives in all state in Nigeria.
Lack of Comprehensive and Adequate Knowledge of Icts
Finally, there is also the lack
of comprehensive and adequate knowledge of ICTs among most information
professionals in tertiary institutions of Ebonyi state. This is detrimental to
the success of digital libraries in Nigeria, more importantly now when the
world is moving towards a knowledge base society where ICTs serves as drivers.
Lack of Acquisition of New Skills and Training of Staff
It is a fact that Librarians need more than basic ICT skills, knowledge and experience to be able to cope with the challenges of managing the digital libraries.
Solutions/Recommendations
The above issues constitute some
of the major stumbling block to the success of digital libraries in tertary
institutions in Ebonyi state. However, within this context this paper highly
recommends that:
Ebonyi state government should give absolute priority to the information sector which is one of the key sectors for societal development. Adequate funds should be provided to libraries for their development and effective functioning. Also all digital library initiatives should be wholeheartedly supported.
The need for involving information professionals in all digital library initiatives. There is the need to intensify the training of such professionals in the area of ICTs, particularly on digitization, digital technologies, as well as web based skills, which are all essential prerequisites for digital library services.
Ebonyi state government should as a matter of urgency address the problems of infrastructures such as electricity and telecommunication networks.Also emphasis should be given to the accessibility and subscription of electronic information resources, locally relevant digitized information resources, as well as free web based information items by digital libraries in tertary institution of the state.
Adequate provision of proper ICT infrastructures such as hardware, software, and international bandwidth e.t.c. should also be given utmost concern. There should be a need for the libraries in tertiary institution of the state to double their efforts in seeking for more funding and support towards the establishment of digital libraries and the upgrading of the existing ones.
From
the above, the following could be recommended:
The virtual library project of the Nigerian University commission (NUC) should be well funded and managed to support the digital libraries in various universities.
Globalization is the main issue for a successful running of the digital library, therefore, there is the need for inter-library connectivity to facilitated information resource sharing in Nigeria.
There is need for Ebonyi state government and other concerned bodies to ensure a unify method of linking Nigeria University libraries together through a particular network.
Since the universities are in the hybrid stage in the country, it is advisable that the University libraries should maintain hybrid collections since our libraries cannot become completely digital in a short while.
University libraries in the state should adopt integrated system based on the latest web 4.0 and other data search and presentation standards which is a unified way of searching and presentation of result.
Conclusion
As
the world is geared and heading towards a knowledge society, the roles of
digital libraries will continue to evolve in this fast changing world without
borders. To conclude, it is imperative to state the digital libraries have
become powerful tools for providing access to networked global information
resources. Therefore, if Nigeria is to play an active role in the global
village, the issue of digital library development should not be handle with kid
gloves. All hands must be on deck to overcome some of the major challenges and
frustrations raised by this paper.The digital libraries today are providing
service utilizing ICT facilities and infrastructures. Though they are faced
with numerous challenges however, the university libraries could gradually
overcome such challenges in the course of time. The most important, librarians
should keep themselves abreast to the new technology and skills of the digital
environment.Ebonyi state E- libraries also need the support of private
establishment, federal and state government to overcome the challenges posed in
the digital environment globalization.
References
- Ani, O. and Edem, N (2012) Trends in the Development of Virtual Libraries in Nigerian
- Universities: A paper Presented at NLA 50th National Conference and Annual
- General Meeting at Abuja. 15th-19th July, 2012.
- Ayo, T.A (2000). Information and Communication Technology and the Information
- Professional in the Information Age: A Compendium of Papers Presented at the 39th
- Annual Conference and AGM at Sam Mbakwe Hall, Imo Concord Hotel, Owerri 17- 22
June.
- Abubakar, A.B. (2009). Education for digital libraries in Asian countries. Paper presented at the Asia-Pacific Conference on Library and Information Education and Practice, (p. 459
- Beagle, D. (1999). Conceptualizing an information commons: The Journal of Academic Librarianship, 25(2), 82-89.
- Burckland Library (2012) Redesigning Library Services: A Manifesto. Chicago: American Library Association
CrossRef - Berry, J.W. (1996). Digital Libraries: New Initiatives with Worldwide Implications. Collection Building, 15(4): 21-33
- Costabile, M. F and Semeraro, G (1998). Information Visualization and the Interaction with IDL. Available at: http//www.ercim.org/publication/DELOS8/costabile.html accessed on 23/04/2014
- Diso, L.I. (2005). Information Technology Policy Formulation in Nigeria: Answers withoutQuestions. International Information and Library Review, 37(4): 295-302
CrossRef - Diso, L.I. (2005). Information production, transfer, and delivery: Mass information work and television Journalists’ dilemma in Nigeria. International Information and Library Review, 37(4), 285-294
CrossRef - Diso, L.I. (2008). Mobile service providers and m-learning in Nigeria: mobility in a contracting space. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM), 2 (1), 40-45
CrossRef
- Daniel, J. O. (2000). “Virtual Library for Nigerian Libraries.” Nigerian Libraries, 36(2): 56.
- Fabunmi B. A. (2009). Challenges and Prospects of Virtual Libraries in Universities in Nigeria:
- European Journal of Scientific Research © EuroJournals Publishing, Inc. 2 009 ISSN
- 1450-216X Vol.33 No.1 (2009), pp.202-208 http://www.eurojournals.com/ejsr.htm
- Gani. E. (2014). Establishment and Management of University Electronic Libraries in Northwest
- Fabunmi, B.A. (2009). Challenges and prospects of virtual libraries in universities in Nigeria. European Journal of Scientific Research, 33(1), 202-208
- Nigerian Universities. MLS Thesis Gbaje, E. (2007). Implementing National Virtual Library for higher institutions in Nigeria:
- Libres library and information technology journal 17(2) pp. 4.
- Ibrahim, U. (2011). Developing search Strategies for effective research output among Staff and Student of Kaduna State University.
- Igu, E (2007). Study Habits of PG Students in Selected Nigerian Universities: Library Philisophy and Practice. Retrieved from http://unlib.unl.edu/LPP/igun-htm retrieved on 24/06/2012
- Gbaje, E.S. (2007). Challenges of Implementing Virtual Library for Higher Institutions in Nigeria. A paper presented at the Conference of the Nigerian Library Association (NLA) (p.42)
- Lesk, M. (2005). Understanding Digital Libraries (2nd ed.) (p.2). San Francisco, CA: Morgan Kaufmann
CrossRef - Mutula, S. (2004). IT diffusion in Sub-Saharan Africa: Implications for developing and managing digital libraries. New Library World, 105 (7/8), 281-289.
CrossRef - Magoi,J.S and Gani,E(2007).The mergence of digital libraries services in Northwest Nigerian universities:challengies and prosepects,Library philosophy and pratical (e-journal).
- Ndukwe, E.C.A. (2005). Furthering the digital revolution in Nigeria in the era of technology convergence. Paper presented at Induction into the Technology Hall of Fame, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria. 11th November, 2005.
- Ogunsola, L.A. (2005). Nigerian University Libraries and the Challenges of Globalization: The Way Forward. Journal of Social Sc
CrossRef

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.