Flexible Channel Allocation for Better Traffic Management in Microcellular Mobile Communication System using Fuzzy logic
G. M. Mir1* , N. A. Lala1
, N. A. Lala1 and A. A. Balkhi2
and A. A. Balkhi2
1College of Agricultural Engineering and Head Information Technology, Srinagar, India.
2S. K. University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir-190025 Shalimar, Srinagar, India.
Corresponding author Email: mir.aspengg@gmail.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojcst11.01.06
Article Publishing History
Article Received on : 20 January 2018
Article Accepted on : 15 February 2018
Article Published : 16 Feb 2018
Article Metrics
ABSTRACT:
Various channels have high traffic density during peak hours the problems are further exacerbated by the traffic overloading in downtown areas at peak hours. The reliable and efficient communication demands unnoticed handoff to the user without deteriorating the signal strength. Current cellular system exhibits a varying traffic conditions depending upon the corresponding variations in population which is low in rural areas and high in downtown areas. The traffic density becomes even higher at peak hours and low at night hours. The acceptable service quality demands optimum use of frequency spectrum for obtaining maximum traffic throughput. The efficient allocation of channels on need basis can be one of the solutions for efficient traffic management during peak hours.
In Flexible Channel Allocation scheme (FlCA), the available channels are divided in fixed and flexible set channels. Fixed set channels are normally assigned to all the cells and the number of channels is decided by the approximate calculated load of particular cell that typically suffices the traffic load of cell. The flexible channels are assigned to those cells whose channels are inadequate under increased traffic load conditions. These channels are assigned in accordance with demand of increased traffic loads. Fuzzy logic approach being flexible is explored for assigning these flexible channels for enhanced QoS.
KEYWORDS:
Channel allocation; Flexible channels; Fuzzy logic; High density traffic
Copy the following to cite this article:
Mir G. M, Lala N. A, Balkhi A. A. Flexible Channel Allocation for Better Traffic Management in Microcellular Mobile Communication System using Fuzzy logic. Orient.J. Comp. Sci. and Technol;11(1)
|
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Mir G. M, Lala N. A, Balkhi A. A. Flexible Channel Allocation for Better Traffic Management in Microcellular Mobile Communication System using Fuzzy logic. Orient. J. Comp. Sci. and Technol;11(1). Available from: http://www.computerscijournal.org/?p=7605
|
Introduction
For the timely allocation of flexible channels the traffic intensity or the blocking probability is continuously measured at every cell site, so that the required cells are assigned to the cell in time when demand arises. The cells can be assigned to cell or released from the cell in accordance with the instant measurement of traffic density and the behavior of traffic with time on prediction basis. The flexible channels are used in identical manner to the assigned fixed channels. No flexible channel is assigned to the cell as long as there are several free fixed channels and traffic density is below certain threshold.1,3 In schedule based flexible channel assignment scheme the traffic conditions, such as movement of traffic peaks in time and space are estimated. The change in assignment of flexible channels is then made at the predetermined corresponding peaks of traffic change. The prioritization of handoff calls based on path codification technique is given in.4
Flexible channel assignment strategies make use of centralized control and require central controller to monitor and have up-to-date information regarding the traffic pattern in its area in order to manage the assignment of the flexible channels. In addition, the scheduled flexible assignment is not adaptive to unexpected changes in traffic. The allocation of variable guard channels to combat handoff calls during high traffic conditions have been described in.5 The decentralized handoff scheme because of corner effect has been given in.6 In case the channels are exhausted and mobile station is moving fast, the handoff can be managed between macro cell and microcell till the target cell is available.7 However, the flexible channel allocation scheme sufficiently reduces the processing load of the system controller as compared to the dynamic channel allocation (DCS) scheme. The number of fixed and flexible channels acting dynamically is monitored and decided by fuzzy logic by acting to the variations of traffic density in the cell. In other wards virtual learning of the system is taking place from the processed data, which eventually resulted from the environmental and traffic changes.
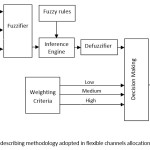
Methodology: Application of Fuzzy-Logic-Based Channel Allocation
At corners of buildings when signal strength of mobile station fades quickly and there are always chances that the call be dropped, so in that condition if no free fixed channel is available there should be flexible channel assigned to the recipient cell to take the call of mobile station.8,9 describes the management of handoff calls due to corner effect fading of signal strength. The block diagram describing the methodology and criteria used in handoff and flexible channel allocation is shown in Figure 1. For implementation of flexible channel allocation scheme different parameters, fixed channels, traffic density and traffic threshold is used as inputs to fuzzy system for decision making about number of channels to be allocated to or relieved from a cell. Fuzzy sets are elements that have a varying degree of membership in a set. Based on the available channels of the neighboring cells a request for allocation of flexible channels is made on demand basis. In case of non-availability of channels the handoffs are queued and served only on the availability of free channels, provided the signal strength does not fall below unacceptable level. The weighting criterion is used to select channels in small, medium or large amounts, which is decided by the nature of traffic growth.
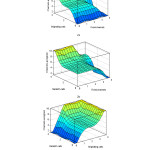 |
Figure 2a: Channels assigned versus originating calls and fixed channels b) Channels assigned versus handoff calls and fixed channels c) Channels assigned versus originating calls and handoff calls
Click here to View figure
|
Results
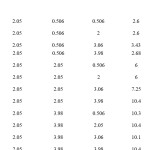
In addition to fixed channels there are guard channels assigned to every cell to cater the demands of handoff calls so that the ongoing calls are not terminated. The assignment of flexible channels is an additional advantage for giving space to the originating calls without disrupting the already ongoing calls. Based on the fuzzy rules are obtained in relationship various input membership functions. The IF-THEN rules are fed to fuzzy inference engine for decision making for assignment of flexible channels in low, medium or high groups in accordance with traffic density conditions. The relationship between membership functions is shown in Table 1. The three dimensional view between various membership functions is given in Figures 2a, 2b, and 2c and gives clear insight between originating calls, handoff calls and channel assignment.
It is observed from data that assignment of flexible channels follows originating calls irrespective of the initial (low, medium or high) fixed channels present in the cell. Since initial fixed channels assigned to a cell is on need basis to handle present traffic in the cell, so the flexible channel assignment is controlled by the system on the bases of demand of traffic conditions in the cell. Thus the increase of traffic by means of originating calls at peak hours needs more channels to be assigned to the cell to combat increased traffic. After the peak time is over the channels will be relieved for further use by any other cell as per requirement. The availability of flexible channels provide continuation of calls as the mobile station travels across cell boundaries.
References
- Yongbing Zhang , Sajal K. Das , Xiaohua Jia, D-CAT., An efficient algorithm for distributed channel allocation in cellular mobile networks, Mobile Networks and Applications. 2004;9(4):279-288.
CrossRef
- Yongbing Zhang , Xiaohua Jia , Sajal K. Das, An efficient approach for distributed channel allocation in cellular mobile networks, Proceedings of the 5th international workshop on Discrete algorithms and methods for mobile computing and communications, Rome, Italy. 2001;87-94.
CrossRef
- F. Valois and V. Veque, “QoS-Oriented Channel Assignment Strategy for Hierarchical Cellular Networks,” Proc. IEEE Int’l Symp. Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Comm. (PIMRC ’00),2000;1599-1603.
CrossRef
- G. M. Mir, N. A. Shah and Moinuddin, Handoffs in Mobile Communication Using Path Codification Technique J. Comp. & Math. Sci. 2013;4(3):135-141
- G. M. Mir, N. A. Shah, Moinuddin, Variable Guard Channels for Efficient Traffic Management International Journal of Electrical, Computer, Energetic, Electronic and Communication Engineering. 2010;4:5:808-812.
- G. M. Mir, N. A. Shah, and Moinuddin, Decentralized Handoff for Microcellular Mobile Communication System using Fuzzy Logic International Journal of Information and Communication Engineering. 2009;5:6:431-435.
- G. M. Mir, Moinuddin, and N. A. Shah, Mobile Velocity Based Bidirectional Call Overflow Scheme in Hierarchical Cellular System International Journal of Electrical, Computer, Energetic, Electronic and Communication Engineering. 2009;3(10):1864-1867.
- G. M. Mir, N. A. Shah, Moinuddin, Realization of QoS in Handoffs by Hysteresis using Fuzzy Logic, Journal of Mass Communicator. 2008;2(2):13-20.
- G. M. Mir, N. A. Shah, Moinuddin, Handoffs for Corner Effects in Microcellular Mobile Communication System, Journal of Mass Communicator. 2009;4(2):19-22.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
 , N. A. Lala1
, N. A. Lala1 and A. A. Balkhi2
and A. A. Balkhi2